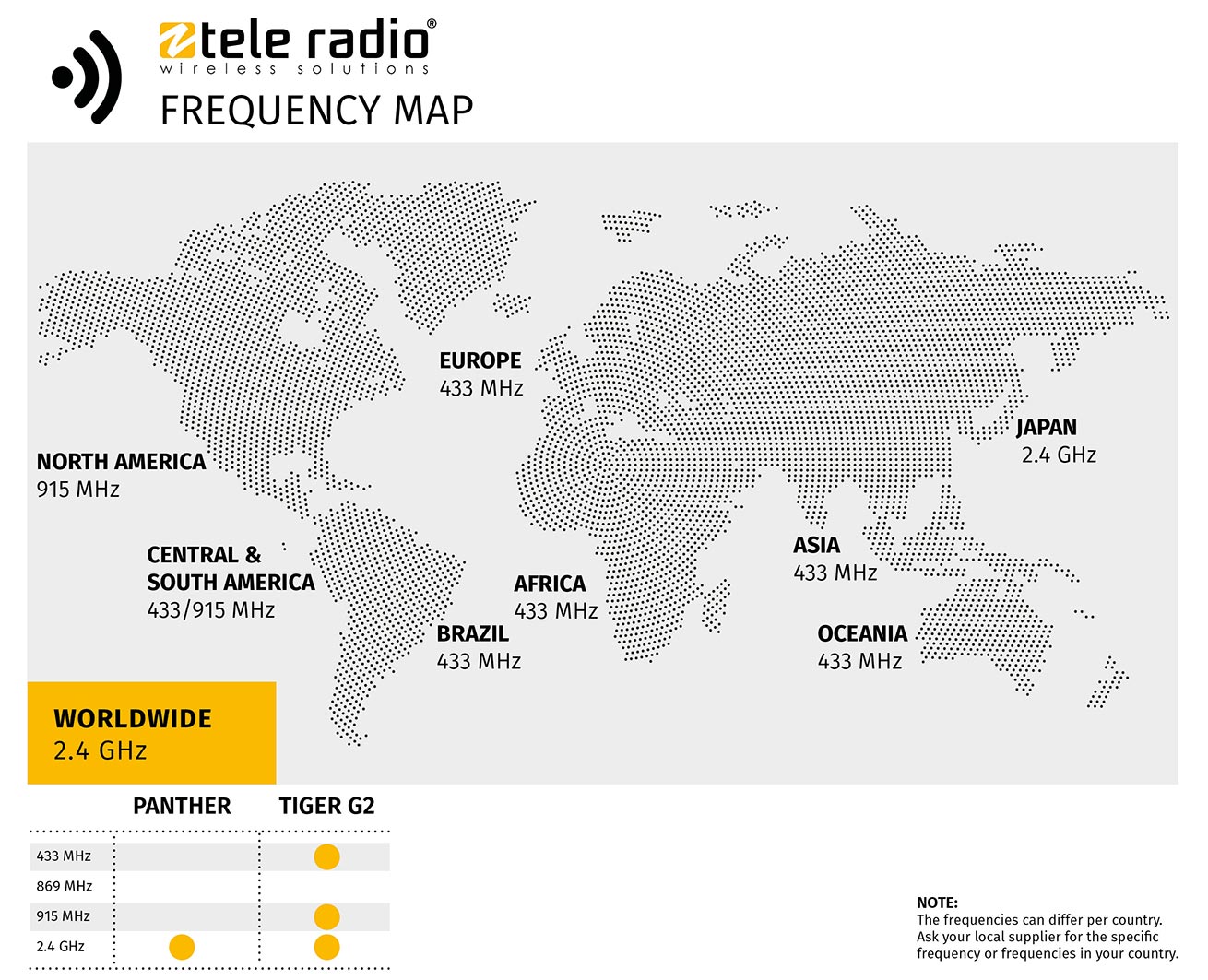
Radio frequency bands used in the world
Blog • Posted on October 1, 2020 at 4:01 pm
Radio bands used for industrial environments (called ISM) differ from continent to continent and from country to country. Tele Radio uses the 433-434MHz, 915MHz and 2400MHz frequencies to meet regulations around the World.
Radiofrequency in the world
Radio frequencies are regulated to ensure that equipment that uses licence free frequencies may be operated safely and according to governing bodies rules. However, each country/continent has its own laws that must be observed when considering the use of radio emitting devices.
The following map illustrates in what country, the before mentioned frequencies are approved/used:
433Mhz
Widely accepted, the 433Mhz frequency is however subject to some local restrictions like in the USA, Japan, Korea, among others. Therefore it is mainly used in the European Market.
This frequency band is recommended if you require great transmission distance between transmitter and receiver.
Multiple systems in the same area, should be set to operate in different frequency channels to avoid interference. Although “cross talk” is not an issue, if two signals meet each other, interference may occur (signals cancelling each other out, causing intermittent or no movement). However, if the signals are coming from the same radio control manufacturer and they meet the standard security regulations (like Tele Radio does) the machine would immediately stop. In no case would a transmitter activate functions in a receiver it isn’t registered to. This security feature is achieved by giving each Transmitter a unique ID code.
915 MHz
While the 915 Mhz frequency is also very popular, it is almost exclusive to the Industrial North American market. When operating in this frequency, it is highly recommended to use FHSS (Frequency-hopping spread spectrum), whereas the Transmitter changes frequencies within a frequency spectrum, in a predetermined pattern every 40 milliseconds, as such avoiding frequency interference to other systems that facilitate the same or similar frequencies.
Universal frequency 2.4GHz
2400MHz (2.4Ghz) is the most broadly accepted frequency around the world.
Products using this frequency usually incorporate DSSS Techonology (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) to avoid frequency interference.
What is DSSS?
DSSS is a spread-spectrum modulation technique primarily used to reduce overall signal interference. The direct-sequence modulation makes the transmitted signal wider in bandwidth than the information bandwidth. After the despreading or removal of the direct-sequence modulation in the receiver, the information bandwidth is restored, while the unintentional and intentional interference is substantially reduced.
How does a transmitter work?

An industrial remote control transmitter is a device that can send information packages in radio waves wirelessly to a receiver by pressing a push button or moving a joystick .
The receiver intercepts the signal with its antenna, interprets the information with its CPU and activates the desired output (relay/transistor/analog etc). This is called simplex communication, as information only travels one way, from transmitter to the receiver.
Information from the machine may also be retrieved wirelessly. This communication is called Duplex communication, which means active communication not only from transmitter to the receiver, but also from the receiver back to the transmitter, information travels in both directions.
Common examples of Duplex Communication are LED feedback, vibration, or showing values like temperature, pressure, speed, etc. on a display screen as part of the transmitter.
In this article you can read more about feedback transmitters.






























 Tele Radio supports the world wide preservation of the Tiger with WWF.
Tele Radio supports the world wide preservation of the Tiger with WWF.